Keeping tabs on your glucose levels is important for controlling one’s health, especially for those diagnosed with either diabetes or prediabetes. Knowing how to monitor your glucose levels is essential in purposeful eating, exercising and taking the medicine prescribed. Here is a comprehensive guide on how to check your blood sugar level accurately.
How To Understand Glucose Levels
To put it simply, glucose is a type of sugar and it is the basic type of energy for the body. Keeping the levels of glucose in check is very important since high and low levels are also heavy in complications on health. By keeping track of one’s glucose levels, these people can steer their course through the intricate balance of these levels.
Normal Glucose Ranges
Fasting Glucose: Normal levels range still between 70 – 99 mg/dL
Post prandial 2 hours after a meal: Normal ranges should be less than 140mg/dL.
Random Glucose Test: Levels below 200mg/dL (higher levels would most probably mean diabetes).
How to Check Glucose Levels
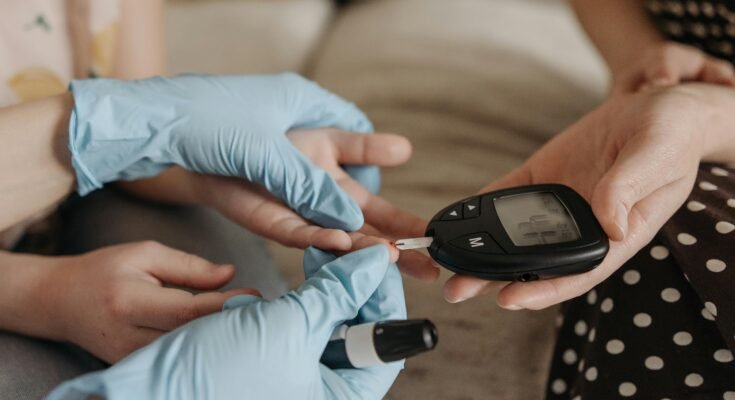
1. Home Glucose Meters
How They Work: A tiny lance pierced the skin, and a droplet of blood, usually from a fingertip, is drawn and placed on the test strip inside the meter. This is the blood glucose level which is displayed on the meter connected to the tray.
Pros: Simple, fast, and effective. Suitable for continuous use.
Cons: Involves purchase of strips, lancets and others. Some users may experience cut from the meddling of the gluing mechanism.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
How They Work: For subcutaneous implant or external wear a specialized device that performs endogenous logic measuring the concentration of glucose in the human body.
Pros: Offers data collection over a period of time, offering better prospects of forecasting and management of glucose levels.
Cons: Costly and might need calibration.
3. Laboratory Blood Tests
Types:
Random blood glucose: is done at any time under random circumstances measuring the level of blood glucose and may not involve fasting.
Postprandial blood glucose test (PPBT): This test measures the glucose level upon the intake of a sugar solution..
Traditional blood haemoglobin
Traditional blood haemoglobin A1c test: A test which indicates how the blood has been in terms of glucose concentration over a period of two to three months.
Pros: Very precise and complete.
Cons: It is time-consuming as well as involves the need to go to a doctor.
4.Urine Tests
Although these tests are not typically done for blood glucose monitoring got glucose concentration that would otherwise be more than what the kidneys could tolerate, urine tests are useful for such and other conditions.
Pros: No invasion to the body.
Cons: Inconclusive and does not give current information.
when is it the most appropriate time to control the blood sugar?
Before Meals: To help regulate insulin or medications such as DPP4 inhibitors.
2 Hours After Meals: Since this is the time when you need to know how your body handles food.
Within 30 min before and 30 minutes after exercising: Important to alleviate changes in blood sugar levels caused by physical activity.
At Bedtime: In order to tackle the issues related to low levels of blood sugar at night.
When Feeling Nauseous or Unwell: Since an illness may cause instability in blood glucose.
How To Make Sure That Measurements Are Done Accurately
Read All Instructions: Before operating a glucose meter or CGM, a user manual should be read for proper use.
Wash Hands First: Unclean hands could lead to contaminated samples and hence, erroneous readings.
Calibrate Devices: Calibration of continuous glucose monitors and other associated devices as appropriate.
Equipment Maintenance: Rehabilitate your equipment for they extend lifespan and precision.
Conclusion
The sociocultural factors which constrain the activities of individuals are emphasized. Diabetics must be able to keep track of their glucose levels if they want to remain in good health. With the correct approaches and at the right time of the day, it is possible to learn a lot about how glucose is distributed and used within the long corridors of one’s body. More than often, updated opinions and recommendations should be associated with healthcare specialists directly responsible for better outcomes for everybody. It is possible to achieve a better control of the illness through lifestyle modification and periodic checkups as they help maintain an even distribution of the sugar levels throughout the body.